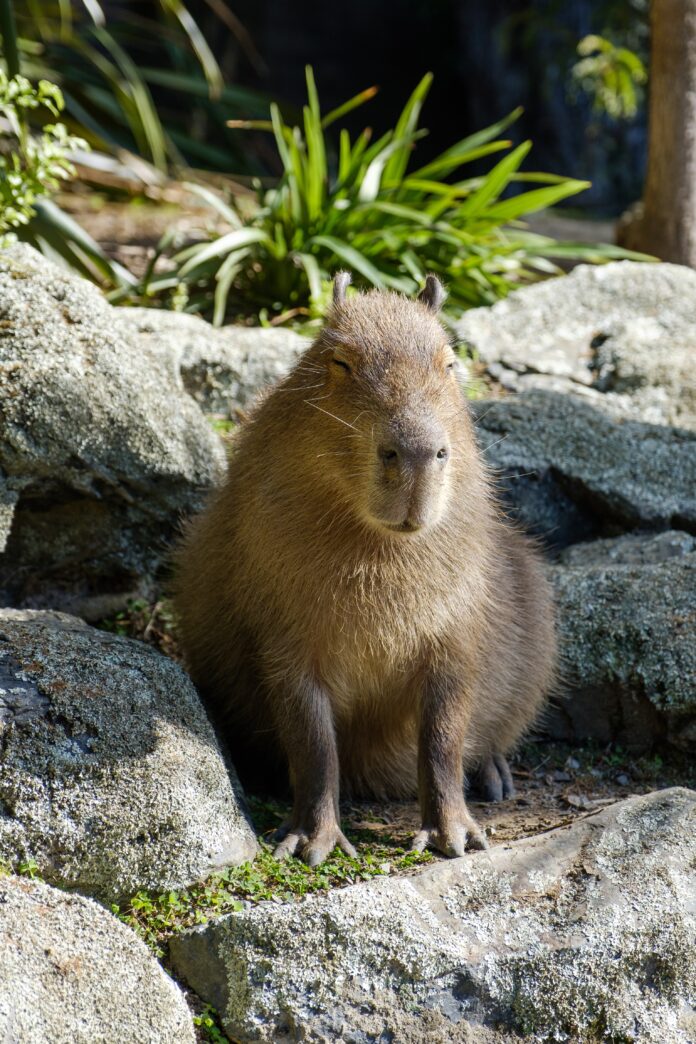
The Capybara is an extraordinary and fascinating creature that captures the attention of animal enthusiasts around the world. With its unique appearance, remarkable characteristics, and intriguing behaviors, the Capybara stands out as one of nature’s most captivating creatures. This article will delve into the world of the Capybara, exploring its physical features, habitat, social structure, diet, and other aspects that make it truly remarkable.
The Capybara, also known by its scientific name Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris, is the largest living rodent in the world. Its name itself, Capybara, exudes a certain charm and curiosity, drawing people to learn more about this extraordinary animal. Native to South America, particularly the vast wetlands of the Amazon Basin, the Capybara thrives in a variety of environments, from lush rainforests to savannahs and marshes. It is a semi-aquatic mammal, perfectly adapted to a life in and around water, making it a truly unique creature among its rodent relatives.
Measuring around one to one and a half meters in length and weighing between 35 to 70 kilograms, the Capybara’s physical appearance is undeniably impressive. Its stocky and barrel-shaped body is covered in a dense, coarse, and reddish-brown fur, which helps protect it from the elements. Capybaras have small, rounded ears and eyes positioned high on their heads, allowing them to keep a watchful eye on their surroundings while submerged in water. Another distinctive feature of the Capybara is its blunt snout, which is ideal for grazing on vegetation and consuming its herbivorous diet.
Capybaras are highly social animals and are often found in large groups known as herds or troops. These herds can consist of anywhere from 10 to 40 individuals, creating a fascinating dynamic within their social structure. Within the herd, there is a clear hierarchy, with a dominant male leading the group and several females and their offspring forming the rest of the community. This social structure provides protection and support, allowing Capybaras to thrive in their habitat.
As herbivores, Capybaras have a diverse and varied diet consisting primarily of grasses, aquatic plants, and bark. Their unique jaw structure and continuously growing incisors enable them to efficiently graze on vegetation, making them important agents in shaping and maintaining their ecosystems. They have a specialized digestive system that allows them to extract as much nutrition as possible from their plant-based diet, further highlighting their remarkable adaptability and ecological significance.
The semi-aquatic nature of Capybaras is perhaps one of their most intriguing traits. They are excellent swimmers and can stay submerged for several minutes, using their webbed feet and partially webbed toes to paddle through the water. Swimming serves multiple purposes for Capybaras, including escaping from predators, regulating body temperature, and finding food sources. In fact, they can even give birth in the water, providing a safe and secure environment for their young.
Predation is an ever-present threat in the animal kingdom, and Capybaras have developed several defense mechanisms to protect themselves from potential predators. Their keen sense of hearing and smell, combined with their ability to quickly retreat into the safety of water, allows them to detect danger and react accordingly. Additionally, Capybaras are known for their alarm calls, emitting loud barks to alert others of potential threats. These collective defense strategies contribute to the survival and well-being of the entire herd.
The Capybara’s reproductive behavior is also of great interest to researchers and wildlife enthusiasts. Breeding usually occurs during the rainy season when food is abundant, and the environment is favorable. Female Capybaras have a gestation period of around 150 days and typically give birth to a litter of three to eight young, known as pups. The newborn pups are remarkably developed, with open eyes and the ability to walk and swim shortly after birth. The entire herd takes part in caring for the young, creating a communal parenting system that ensures the survival and well-being of the offspring.
The Capybara is an enchanting creature that captivates the imagination with its unique physical features, intriguing behaviors, and remarkable adaptability. From its impressive size and semi-aquatic nature to its highly social structure and diverse diet, the Capybara has carved its place in the animal kingdom as a fascinating and essential species. By understanding and appreciating these incredible creatures, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the wonders of the natural world and the intricacies of its inhabitants, such as the extraordinary Capybara.
Throughout history, the Capybara has played a significant role in the lives of humans. Indigenous cultures in South America have long recognized the value of these animals, both as a food source and for their durable hide, which can be used to make various products. In some regions, Capybaras are even kept as pets, thanks to their gentle and sociable nature.
As human populations continue to expand and encroach upon the natural habitats of Capybaras, conservation efforts become increasingly important. These animals are currently listed as “Least Concern” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), but certain localized populations may face threats due to habitat loss, hunting, and competition with domestic livestock. In order to ensure the long-term survival of Capybaras, it is crucial to protect their habitats, enforce hunting regulations, and raise awareness about the ecological importance of these unique creatures.
Scientists and researchers are also actively studying Capybaras to gain a deeper understanding of their biology, behavior, and ecological impact. Through field observations, captive studies, and genetic research, valuable insights are being gained into the social dynamics of Capybara herds, their feeding habits, and their role in shaping the ecosystems they inhabit. This knowledge contributes not only to our understanding of Capybaras but also to the broader field of ecology and wildlife conservation.
In popular culture, Capybaras have garnered attention and adoration for their unusual appearance and gentle demeanor. They have become social media sensations, with countless adorable pictures and videos showcasing their unique charm. Their docile nature and affinity for water have also made them popular attractions in zoos and wildlife parks around the world. Visitors have the opportunity to observe these magnificent creatures up close and learn about their fascinating behaviors.
In summary, the Capybara is an extraordinary animal that captivates our imagination with its physical attributes, social structure, and adaptability. From its prominent presence in South American ecosystems to its interaction with humans and its growing popularity in popular culture, the Capybara continues to leave an indelible mark on our collective consciousness. By appreciating and protecting these remarkable creatures, we not only ensure their survival but also deepen our understanding of the diverse and interconnected web of life on our planet. The Capybara truly exemplifies the wonders of the natural world and serves as a reminder of the beauty and diversity that surrounds us.